Video Timings: VGA, 720p, 1080p
To work with standard monitors and TVs, you need to use the correct video timings. This guide includes the timings for many standard display modes using analogue VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort: 640x480 (VGA), 800x600 (SVGA), 1024x768 (XGA), 1280x720, and 1920x1080 (30 Hz and 60 Hz).
CRT monitors typically support higher refresh rates in addition to 60 Hz, such as 72 and 85 Hz, but most LCD monitors do not. There are an increasing number of televisions and monitors that do support high refresh rates, but these are beyond the scope of this guide.
Use these timings at your own risk. Modern display are generally tolerant, but an out-of-spec signal can damage fixed-frequency CRTs.
Contents
- Video Signals in Brief
- Understanding Video Timings
- 640x480 60 Hz
- 800x600 60 Hz
- 1024x768 60 Hz
- 1280x720 60 Hz
- 1920x1080 60 Hz
- 1920x1080 30 Hz
Video Signals in Brief
Video signals have two phases: drawing pixels and the blanking interval. The sync signals occur within blanking intervals; separated from pixel drawing by the front porch and back porch. Horizontal sync demarcates a line and vertical sync a frame.
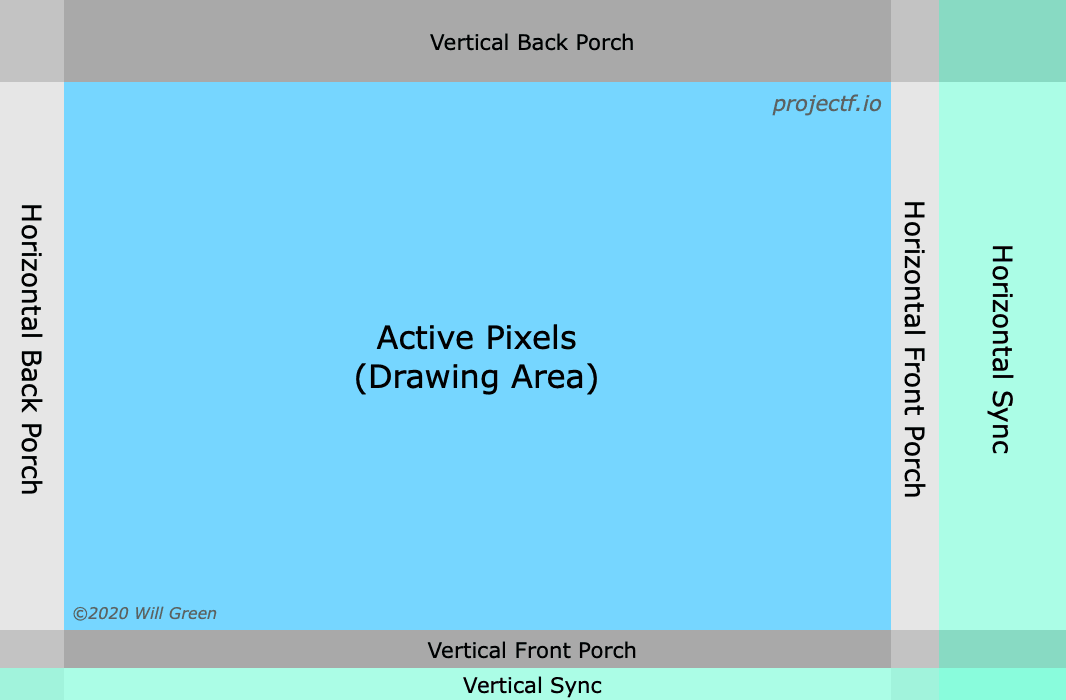
Understanding Video Timings
Video timings are a complex area with multiple standards from the computer and consumer electronics (TV) industries. For example, on the computer side we have VESA Coordinated Video Timings (CVT), which includes four variants for common HD resolutions, each of which require a different pixel clock.
This document avoids this complexity by providing conservative timings that work with most displays. These timings are based on VESA DMT v1.3 (available from vesa.org) and CTA-861-G (available from cta.tech). Other data, such as bandwidths and memory requirements are calculated by the author.
Reduced Blanking
VESA Coordinated Video Timings (CVT) include reduced blanking (RB) interval variants. Reduced blanking is attractive because it lowers clock frequencies and peak bandwidth requirements. For example, 1280x720p60 CVT-RBv2 has a pixel clock of 60.465 MHz vs 74.25 MHz for the CTA version. When you’re struggling to meet timing on your FPGA design, these lower clocks look inviting.
Despite the advantages of reduced blanking, I don’t recommend it when developing your own hardware. Reduced blanking timings have a much tighter clock tolerance of ±0.001 MHz and aren’t generally supported by televisions. Even if you’re sticking to computer monitors, you can’t be sure if an arbitrary monitor will handle your chosen timing.
For small-scale projects, reduced blanking is only viable if you’re targetting a single display model.
Additional Data
For each display mode I’ve provided additional helpful data for developing you own hardware.
The frame memory values show how many kilobits (divide by 8 for bytes) of memory you need to store a single frame; 12-bit per pixel equates to 4:2:0 Y’CrCb.
The data rate is the required bandwidth for 24 bits-per-pixel with the included timings.
DVI & HDMI use TMDS encoding: the TMDS clock shown is for regular 24-bit colour; higher colour depths require higher frequency clocks.
VIC is the Video Identification (ID) Code used in EDID.
640x480 60 Hz
640x480 is one of the classic VGA resolutions and became the lowest common denominator for computer displays in the early 1990s. 640x480 works with analogue VGA monitors and most contemporary HD displays and televisions. I recommend starting with 640x480 when developing your own hardware; it’s almost foolproof and requires much lower clock speeds than HD resolutions.
The historical VGA standard calls for a 25.175 MHz pixel clock, which isn’t always easy to generate via PLL. Many people use 25 MHz and find it works fine. Based on the VESA pixel clock tolerance of 0.5%, 25 MHz is unacceptable, though I haven’t found this to be a problem in practice.
My recommendation is to go for 25.2 MHz; it’s relatively easy to generate, is within VESA tolerance, and gives an exact 60 Hz refresh rate (rather than 59.5 MHz at 25 MHz).
Beginning FPGA Graphics includes SystemVerilog designs using this display mode.
Name 640x480p60
Standard Historical
VIC 1
Short Name DMT0659
Aspect Ratio 4:3
Pixel Clock 25.175 MHz
TMDS Clock 251.750 MHz
Pixel Time 39.7 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 31.469 kHz
Line Time 31.8 μs
Vertical Freq. 59.940 Hz
Frame Time 16.7 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 640
Front Porch 16
Sync Width 96
Back Porch 48
Blanking Total 160
Total Pixels 800
Sync Polarity neg
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 480
Front Porch 10
Sync Width 2
Back Porch 33
Blanking Total 45
Total Lines 525
Sync Polarity neg
Active Pixels 307,200
Data Rate 604.2 Mbps
Modeline "640x480_60" 25.175 640 656 752 800 480 490 492 525 -HSync -VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 300
8-bit Colour 2,400
12-bit Colour 3,600
24-bit Colour 7,200
32-bit Colour 9,600
NB. Porch times shown include the border times referenced in VESA DMT.
800x600 60 Hz
800x600 (AKA SVGA), offers a little over 50% more pixels than 640x480. The pixel clock for 800x600 is precisely 40 MHz, which is easy to generate via PLL on most FPGAs.
Name 800x600p60
Standard VESA DMT
VIC N/A
Short Name N/A
Aspect Ratio 4:3
Pixel Clock 40.000 MHz
TMDS Clock 400.000 MHz
Pixel Time 25.0 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 37.897 kHz
Line Time 26.4 μs
Vertical Freq. 60.317 Hz
Frame Time 16.6 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 800
Front Porch 40
Sync Width 128
Back Porch 88
Blanking Total 256
Total Pixels 1056
Sync Polarity pos
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 600
Front Porch 1
Sync Width 4
Back Porch 23
Blanking Total 28
Total Lines 628
Sync Polarity pos
Active Pixels 480,000
Data Rate 960.0 Mbps
Modeline "800x600_60" 40.00 800 840 968 1056 600 601 605 628 +HSync +VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 469
8-bit Colour 3,750
12-bit Colour 5,625
24-bit Colour 11,250
32-bit Colour 15,000
1024x768 60 Hz
1024x768 (AKA XGA) was a popular 4:3 resolution for CRT monitors and is still available in LCD panels. 512x384 is useful graphics resolution when working with this display mode.
Name 1024x768p60
Standard VESA DMT
VIC N/A
Short Name N/A
Aspect Ratio 4:3
Pixel Clock 65.000 MHz
TMDS Clock 650.000 MHz
Pixel Time 15.4 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 48.363 kHz
Line Time 20.7 μs
Vertical Freq. 60.004 Hz
Frame Time 16.7 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 1024
Front Porch 24
Sync Width 136
Back Porch 160
Blanking Total 320
Total Pixels 1344
Sync Polarity neg
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 768
Front Porch 3
Sync Width 6
Back Porch 29
Blanking Total 38
Total Lines 806
Sync Polarity neg
Active Pixels 786,432
Data Rate 1.560 Gbps
ModeLine "1024x768_60" 65.00 1024 1048 1184 1344 768 771 777 806 -HSync -VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 768
8-bit Colour 6,144
12-bit Colour 9,216
24-bit Colour 18,432
32-bit Colour 24,576
1280x720 60 Hz
The lowest of the common HD resolutions, 720p is widely supported and has relatively modest bandwidth requirements: an 8-bit 720p display requires less than 8 Mbits per frame. Note how the pixel clock of 720p is the same as 1080p30 and half that of 1080p60: this simplifies your design if you need to support both resolutions.
Name 1280x720p60
Standard CTA-770.3
VIC 4
Short Name 720p
Aspect Ratio 16:9
Pixel Clock 74.250 MHz
TMDS Clock 742.500 MHz
Pixel Time 13.5 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 45.000 kHz
Line Time 22.2 μs
Vertical Freq. 60.000 Hz
Frame Time 16.7 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 1280
Front Porch 110
Sync Width 40
Back Porch 220
Blanking Total 370
Total Pixels 1650
Sync Polarity pos
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 720
Front Porch 5
Sync Width 5
Back Porch 20
Blanking Total 30
Total Lines 750
Sync Polarity pos
Active Pixels 921,600
Data Rate 1.782 Gbps
Modeline "1280x720_60" 74.25 1280 1390 1430 1650 720 725 730 750 +HSync +VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 900
8-bit Colour 7,200
12-bit Colour 10,800
24-bit Colour 21,600
32-bit Colour 28,800
1920x1080 60 Hz
The 1080p HDMI television or monitor has been the dominant specification for some years. If you’re only going to support one resolution, then 1920x1080p60 is a solid choice. However, you should bear in mind that the TMDS clock is almost 1.5 GHz, which is demanding for non-transceiver I/O. A full 32-bit 1080p display requires just under 64 Mbits per frame.
1920 and 1080 have many common divisors, so you can support many lower graphics resolutions within 1080p using integer scaling: 80x45, 96x54, 128x72, 160x90, 192x108, 240x135, 320x180, 384x216, 480x270, 640x360, and 960x540.
Name 1920x1080p60
Standard SMPTE 274M
VIC 16
Short Name 1080p
Aspect Ratio 16:9
Pixel Clock 148.5 MHz
TMDS Clock 1,485.0 MHz
Pixel Time 6.7 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 67.500 kHz
Line Time 14.8 μs
Vertical Freq. 60.000 Hz
Frame Time 16.7 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 1920
Front Porch 88
Sync Width 44
Back Porch 148
Blanking Total 280
Total Pixels 2200
Sync Polarity pos
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 1080
Front Porch 4
Sync Width 5
Back Porch 36
Blanking Total 45
Total Lines 1125
Sync Polarity pos
Active Pixels 2,073,600
Data Rate 3.564 Gbps
ModeLine "1920x1080_60" 148.50 1920 2008 2052 2200 1080 1084 1088 1125 -HSync -VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 2,025
8-bit Colour 16,200
12-bit Colour 24,300
24-bit Colour 48,600
32-bit Colour 64,800
1920x1080 30 Hz
If you want full HD resolution at the lowest possible pixel clock and bandwidth, consider 1080p30.
1080p30 has the same 1920x1080 resolution and timings as 1080p60 but half the pixel clock. Using the same pixel clock as 720p60 makes supporting both resolutions trivial in FPGA logic.
The main downsides of this mode are its poor handling of rapid motion (such as a mouse pointer) and that it might not be recognised by some computer displays.
Name 1920x1080p30
Standard SMPTE 274M
VIC 34
Short Name 1080p30
Aspect Ratio 16:9
Pixel Clock 74.250 MHz
TMDS Clock 742.500 MHz
Pixel Time 13.5 ns ±0.5%
Horizontal Freq. 33.750 kHz
Line Time 29.6 μs
Vertical Freq. 30.000 Hz
Frame Time 33.3 ms
Horizontal Timings
Active Pixels 1920
Front Porch 88
Sync Width 44
Back Porch 148
Blanking Total 280
Total Pixels 2200
Sync Polarity pos
Vertical Timings
Active Lines 1080
Front Porch 4
Sync Width 5
Back Porch 36
Blanking Total 45
Total Lines 1125
Sync Polarity pos
Active Pixels 2,073,600
Data Rate 1.782 Gbps
Modeline "1920x1080_30" 74.25 1920 2008 2052 2200 1080 1084 1089 1125 +HSync +VSync
Frame Memory (Kbits)
1-bit Colour 2,025
8-bit Colour 16,200
12-bit Colour 24,300
24-bit Colour 48,600
32-bit Colour 64,800
What about 4K?
The author doesn’t (yet) have 4K-capable FPGA boards, so hasn’t tested timings for 4096×2160 (DCI 4K), or 3840x2160 (4K UHD). Sorry.